Nature and Chemistry 2

Author(s):
Summary:
9.5.1.1. Explains the importance of water for assets. 9.5.1.2. Develops solutions for saving water and protecting water resources. It is a lesson plan developed for these gains. The aim of this lesson plan is to explain the importance of water resources and protection, and to emphasize that the efficient use of water is the responsibility / duty of every citizen towards his country and the world.
| Subject | Green Chemistry / Green Biotechnology / Green Engineering and Robotics |
| Topic | Water and Life |
| Age of students | |
| Preparation time | 15 Minutes |
| Teaching time | 2*40 Minutes |
| Online teaching material (links for online material) | |
| Offline teaching material |
Aim of the lesson
· At the end of this course, students will be able to:
1)Understand the importance of protecting water resources.
2) Discover that it can take advantage of technology to reduce water consumption.
3) Predict what dangers await the world as a result of excessive consumption of natural resources.
4) Make designs that will reduce water consumption with robotic coding.
Activities
Describe here in detail all the activities during the lesson and the time they require. Remember, that your lesson plan needs to revolve around the topic of green engineering and robotics.
| Name of activity | Procedure | Time |
| Engage-1 | The teacher comes to the classroom and after asking the students how they are, makes a short review on the topics covered in the previous lesson. Then, the teacher shows the students the following visuals and asks the question “Why did technology develop in this way?” The answers given by the students individually are written on the board. | |
| Explore-1 | At this stage, the teacher asks the students to draw a schematic representation of the water cycle they have learned in the past years. Later, he gives a brief information about the water cycle and explains that this cycle has suffered worldwide disruptions in recent years and this is caused by global warming. Then he asks the students “What are the solutions in technology due to these problems?” and wants them to give an example verbally. Some images are presented to the students by teacher to support the examples given. | |
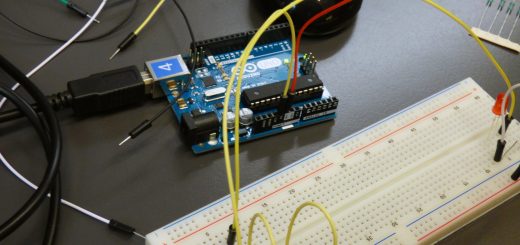
| Explain-1 | Water Saving Faucet Materials List to Use:1. Arduino Robotic Coding Board2.1 Piece IR Led Sensor3.1 piece 24V Solenoid Valve4.1 Piece 5V Relay5.1 Voltage Adjustable Adapter6.1 Breadboards7.Jumper Cable8.Mblock IDE program Arduino Uno 2. IR Led Sensor 3. 24V Selenoid Valve 4. 5V Relay 5. Adapter 6. Breadboard 7. Jumper Cable 8. Mblock IDE Data to be Obtained:A water-saving faucet will be made in our project setup. First, a student will brush a tooth in a tap that does not save water, and water will be collected in a container that will be put down. Here the accumulated water level will be measured. Second, he will brush his teeth in the water-saving faucet and the level of water accumulated in the container will be measured. The data to be obtained will be the water level. Expectation:Since the water-saving faucet will operate as long as the student reaches out to the faucet, there will be no wasted water flow. It is expected that less water will accumulate in the container to be placed under the energy saving tap compared to the other mechanism. Thus, consumption of natural resources will be less and water savings will be achieved. | 5 min |
| Elaborate-1 | Water and Life Water is one of the basic needs of living life. All living things need water to survive and thrive. Because water constitutes a large part of living organisms. For example, water constitutes 70% of the human body by mass and 60% of trees by mass. Biological reactions that occur in living cells take place in aqueous solutions.Especially humans, among the creatures in nature, rapidly pollute the water resources scattered irregularly on the earth’s surface, reducing the possibility of usability. Availability of usable water in nature varies greatly according to time and place. For this reason, the water on earth is divided into two as sea water and fresh water.Most of the water resources in the world are located in oceans and seas. When fresh water resources in the world are evaluated, it can be said that groundwater constitutes 75% of fresh water resources. Groundwater constitutes all available water resources:Groundwater 95%Lakes and rivers 3.5%Soil moisture 1.5%Water resources can be classified into four different groups in general.Surface waters: Lakes, rivers, streams, seas and oceansAtmospheric waters: Snow, hail and rainGroundwaterCosmic waters: Waters that come from space by meteorites.The cycle of water between atmosphere, land, and oceans is called the water cycle. The water cycle is an open system powered by solar energy. Glaciers, oceans, seas, lakes and rivers make up the bulk of the water on earth. WATER RESOURCESWater exists in different physical states in the world. It is in the form of vapor in the atmosphere, as glaciers in the poles and high mountains, and in liquid form in sea, lake, river and groundwater. Not all water in the world is drinkable. Therefore, waters and resources are divided into two main groups as fresh water and salt water.Fresh waters: 3% of the total water in the world.Salty waters: 97% of the total water in the world.Waters containing less than 0.05% salt by mass are called fresh water, and waters containing more than 0.05% salt by mass are called salty water.Salty Water: Salty water that cannot be used as drinking water constitutes 97% of the water in the world. Salty water resources in the world:OceansThe seasSalt lakes.Fresh Waters: Only 3% of the water resources in the world are fresh water. Fresh water resources and their proportion in fresh water are as follows:Glaciers (68.3%)Groundwater (31.4%)Surface waters (0.3%)Glaciers: They are masses of snow and ice that do not melt in summer and winter. Glaciers are found in polar regions and high mountain peaks. They constitute 68.3% of fresh water resources.Groundwater: Water that is stationary or in motion below the surface. They constitute 31.4% of fresh water resources.Surface waters: These are lakes, streams and swamps. They constitute 0.3% of fresh water resources. Protection of Water ResourcesFresh water resources in the world are both less and their distribution is different. While water waste is very high in some parts of the world, there is famine in some parts of the world. With the development of industry and unconscious wastes, fresh water resources are rapidly becoming polluted and losing its feature of being a usable resource. Therefore, approximately hundred thousands of people die each year from diarrheal diseases. Since water is valuable and scarce, fresh water resources should be protected and waste should be avoided in water use.To avoid wasting water, the following can be applied.Faucets shouldn’t leak or drip.In the bathroom, washing with a shower should be preferred instead of filling the bathtub with water.The faucet should not be left open while shaving, washing hands, brushing teeth.Places such as cars and balconies should be cleaned not with a hose, but by wiping or using a bucket and sponge.Garden irrigation should be done in the morning or evening hours when evaporation is less.Washing clothes and dishes in the machine should be preferred instead of hand washing. Design of Experiment Setup: In our experiment, a faucet to provide water flow will be used. When someone who wants to wash his hand extends his hand, an IR sensor will detect this hand, and a relay and solenoid valve will be used to control this tap when the hand is detected. In addition, a container will be used to collect the used water, and the level of the accumulated water in this container will be measured. The Editing of the Experiment: The experimental setup will be designed. ●When someone who wants to wash their hands comes, the IR sensor will detect this hand and send a signal to the Arduino Robotic Coding card.●The signal from the IR sensor will be transmitted to the relay via Arduino and the solenoid valve will be opened.● When the hand is pulled under the faucet, the IR sensor will detect it and send a signal to the Arduino Robotic Coding card.● The signal from the IR sensor will be transmitted to the relay via Arduino and the solenoid valve will be closed.● Under the tap, there will be a container for water to accumulate and the water level will be measured in this container.● The information coming from the IR sensor will be sent to Arduino, and Arduino will send this information to the computer via the USB Serial port. Necessary materials:1 x Arduino Uno Robotic Coding Board1 x Breadboard1 x IR Led Sensor1 x 24V Solenoid Valve1 x Adapter1x 5V Relay5 x Jumper cable1 x Wide shallow bowl Introduction of Solenoid Valve and Pin Connections:By the mechanism inside the solenoid valve is tool that can open and close with the mechanism inside it. There are 2 pinouts available, these areVcc, GND. When operating voltage is given from pins,the valve will work. To define the functions of the pin outputs: Vcc: The pin where the voltage is supplied to. It is required for device operation. GND: Required pin forcompleting the electrical circuit Introducing IR Led Sensor and Pin Connections: Making relay connections Relay is a circuit element that is used to open and close circuits that require high power by using low power. When we digitally give 1 to the relay from the Arduino Robotic Coding Board, it closes the circuit and provides energy to the place where it should be transmitted. When the relay is given 0 from Arduino, the circuit is opened and the energy is not given, the device at the end of the relay does not work. In this project, the opening and closing of the led solenoid valve will be provided using this method. To define the functions of the pin outputs: Vcc: The pin to be connected to the Analog input of ArduinoGND: pin to be connected to the GND ends of ArduinoSignal: the pin to be connected to Arduino’s digital outputC: the pin One end of the cable to be joined will be connectedNO: The pin the other end of the cable to be joined will be connected Here, with the command sent from Arduino to the relay’s signal pin, the C and NO pins will be closed or opened. Thus, the solenoid valve connected to the relay terminal will be controlled. Making Circuit Connections:First of all, as mentioned above, a container will be placed under the tap to collect water. As a result of the experiment, the level of water accumulated in the container will be measured. An IR sensor will be placed to detect the movement of the hand, a relay and a solenoid valve will be placed to control the water tap. The relay will be powered by a 12V adapter. Circuit connection will be made as follows. 1. The connections of the solenoid valve that will control the tap will be made as follows. Valve Pins Arduino Pins Vcc Vcc (To activate the device) GND GND (To complete the power circuit) 2. The connections of the IR Sensor placed to detect the hand movement placed in front of the tap will be made as follows. IR Sensor Pins Arduino Pins Vcc Vcc (To activate the device) GND GND (For the completion of the power circuit) Digital D2 (for detecting motion) 3. The relay connections that will allow us to control the solenoid valve are as follows: Relay Pins Arduino Pins Vcc Vcc (To activate the device) GND GND (For the completion of the power circuit) Signal D3 (for 1/0 information) Coding for saving faucet The application we will use for coding is the Mblock program. This application is a tool that allows us to do robotic coding by dragging and dropping blocks without the need for programming language knowledge. Coding block is below. 2 coding will be made for our project. First, coding will be done as a saving tap. Here, water will flow when the student’s hand reaches out to the tap. The application we will use for coding is the Mblock program. This application is a tool that allows us to do Robotic coding by dragging and dropping blocks without the need for programming language knowledge. The coding block is shown above. If we explain the application steps one by one: Digital Pin Reading () block: Indicates that data from the given Digital pin of Arduino () in parentheses are read. Data from digital pins can only be 0 or 1. In this project, data from digital pin 2 is read. ( ) ile ( ) comparison block: This block compares two values in parentheses. If they are same, it results “True” or 1, if they are not equal, it turns “False”or 0. In this project data read from digital pin 2 is compared with 0 value. If () then, else block: If the expression that comes in parentheses with this block of code is logically “True”, all blocks placed in the block work. If it is logically “False”, this and the code blocks in it are passed without running. This block refers to the pin number given in parentheses.It provides sending the value 1 or “True” to the pin number given in parenthesis from Arduino. By sending a command from the pin 3 of Arduino to the SIGNAL pin of the relay, it turns off the valve circuit and it makes the valve work. set the digital pin “low” block: This block refers to the pin number given in parentheses.It provides sending the value 0 or “False” to the pin number given in parenthesis from Arduino. By sending a command from the pin 3 of Arduino to the SIGNAL pin of the relay, it turns on the valve circuit and it makes the faucet close. Forever block: As long as Arduino is open, it provides continuous repetition of the blocks placed in it. This process will be done continuously unless Arduino is closed. The block when Arduino Uno starts: This block represents energizing the Arduino Robotic Coding device. It means that code blocks added as a chain will be executed when energized and started to run. ● As a chain to the “Arduino Program” block, “continuous repeat block” is added so it will be entered into this block first. ● In the continuous repeat block, the “if – else” block will be queried as a chain block. Here, the condition in parentheses is questioned. In parentheses, the equality of the data from Digital Pin number 2 with 0 is questioned. If equal, it is entered into the block. ● Entering the “if () if ()” block means that a motion is detected. In this case, the relay connected to pin number 3 will be made high. In other words, the tap will be opened. ● If it is not in the “if () if-not” block, if it works, that means the motion sensor did not detect any motion. In this case, the low connected to pin number 3 will be made. In other words, the faucet will be closed. Coding for Normal Faucet: With the coding from this part of the project, we will operate the faucet in a way that does not save water. There will be a flow of water for 120 seconds after the student takes his hand. If we explain the application steps one by one: In this section, different commands from the first codes will be introduced. If () then, else block: If the expression that comes in parentheses with this block of code is logically “True”, the blocks placed in the first block work. If it is logically “False”, the codes in the second block work. Block until ():Until this block reaches the value given in brackets, makes the code in the block run. When reached to the entered value, the block exits. Reset timer:When this block command starts running, time is reset and time starts from the beginning. Timer> () block:When the previously reset time is greater than 120 seconds, this line of code will be complete. Here a comparison between time and seconds has been made. () sec wait block:When the continuous repeat block is entered, after 1 second the command below will be passed. | 25+25 min |
| 5. Evaluation | After the subject summary is given by the teacher by way of presentation, the students are asked to write a composition that explains what problems await us in the next century if we do not use water efficiently. Vey good (10)pointsgood(8)pointsmedium(6)pointsacceptable(4)pointspoor(2)pointsMaking use of different scientific sources while preparing the composition. The flow of the composition (introduction-development-result). Defining the problem clearly in the composition Presenting a clear solution to the problem in composition Working in harmony with teammates Being able to present the composition to classmates Presenting examples from daily life regarding the problem The originality of the solution created Applicability of the solution method produced Using language correctly in composition | x min |
| X min |
Assessment
Describe here the assessment method of the lesson, if any. For example, if you plan on assessing your students with a quiz, include here questions and answer options with color-coding the correct answers.